Cloud infrastructure is the combination of hardware and software, including servers, storage, networking, and virtualization tools, that supports cloud computing. This framework enables businesses to deploy, manage, and scale applications without relying on physical, on-premises systems.
Once dependent on costly data centers and complex scaling procedures, companies now access computing resources instantly through flexible cloud models, such as public, private, or hybrid, managed entirely by cloud infrastructure providers. These providers ensure built-in security, high availability, and seamless scalability, allowing businesses to focus on innovation rather than infrastructure maintenance.
The evolution from traditional IT to cloud-based operations has redefined how organizations handle performance, accessibility, and cost control. Service models like IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, and FaaS empower teams to launch faster, reach global users, and operate with greater efficiency.
Whether supporting startups building applications or enterprises running mission-critical systems, cloud infrastructure delivers the resilience and agility modern businesses demand. Reflecting this shift, Precedence Research projects the U.S. cloud infrastructure market will grow to USD 252.12 billion by 2034, underscoring its role as the foundation for digital transformation across industries.
Table of Contents
How Does Cloud Infrastructure Work?
Cloud infrastructure operates through a combination of virtualization, physical servers, and globally distributed data centers to deliver scalable, on-demand computing power. Cloud providers run multiple virtual machines on a single server, managed through advanced cloud management platforms that streamline resource allocation and performance monitoring. This model enables businesses to leverage efficient cloud infrastructure services without investing in or maintaining physical hardware, making operations more agile and cost-effective.
A key feature of cloud-based infrastructure is elasticity, the ability to scale resources automatically based on demand. With integrated cloud and infrastructure tools, organizations can ensure high availability, security, and performance while avoiding overprovisioning. Providers also handle system maintenance and updates, allowing companies to focus on growth while robust cloud management ensures seamless deployment, monitoring, and optimization across global environments.
What Are the Key Components of Cloud Infrastructure?
The key components of cloud infrastructure include servers, networking, storage, and software, which work together to deliver computing resources efficiently. These components of IT infrastructure ensure scalability, security, and reliability, allowing businesses to optimize performance and reduce IT overhead. Understanding how these elements function helps organizations leverage cloud solutions effectively.
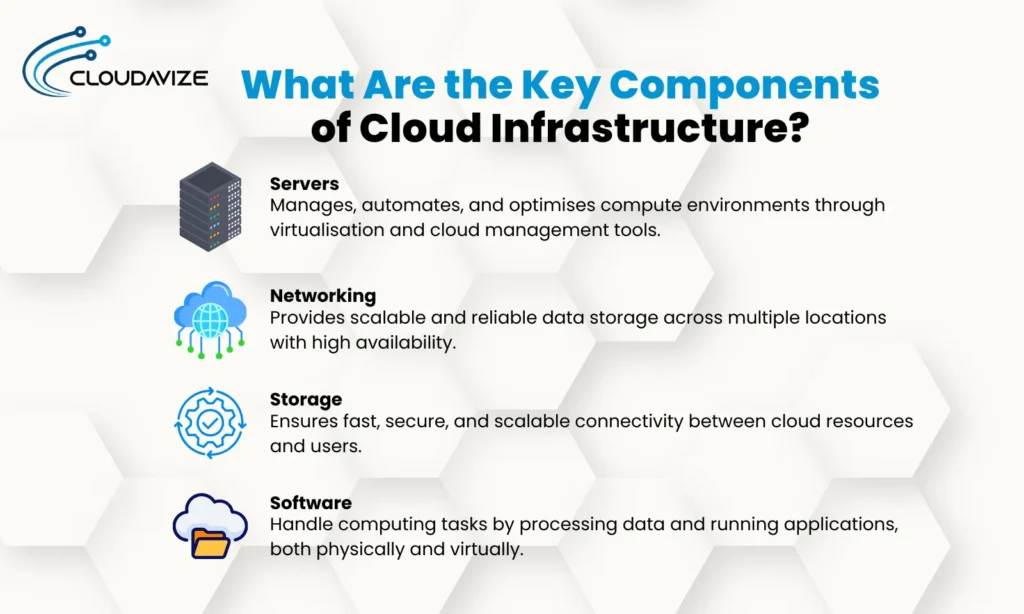
Servers
At the core of the cloud infrastructure, servers handle computing tasks by processing workloads and running applications at scale. Within modern cloud and infrastructure setups, these servers are housed in secure data centers and are virtualized to allow multiple computing environments to run simultaneously on shared physical resources. This virtual layer maximizes efficiency and supports high-performance computing without hardware constraints.
Leading cloud infrastructure services providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud deploy massive fleets of servers across global regions to ensure low-latency access, load balancing, and fault tolerance. Through cloud management platforms, organizations can easily allocate or reassign server resources, enabling seamless scalability and optimized cost control within a cloud-based infrastructure environment.
Networking
A robust cloud network is a critical component of cloud infrastructure that ensures fast, secure, and scalable connectivity between applications, databases, storage systems, and users. A strong cloud and infrastructure network ensures fast data transfer, low latency, and reliable access across regions. It also facilitates hybrid cloud models where on-premises systems interact with cloud-based infrastructure in real time.
Advanced technologies like software-defined networking (SDN), load balancing, firewalls, and VPNs enhance performance and security. These features are centrally managed through cloud management tools that monitor traffic, apply security rules, and scale bandwidth as needed. An optimized network architecture supports global cloud operations while maintaining performance, reliability, and security standards.
Storage
Cloud storage solutions enable businesses to store, access, and manage massive volumes of data with high availability and reliability. Businesses can store structured or unstructured data across geographically distributed locations, ensuring redundancy and minimizing the risk of data loss. The flexibility of cloud-based infrastructure allows organizations to choose the best storage model based on workload requirements.
The three primary types of cloud storage are
- Object storage: Ideal for large, unstructured datasets like images and videos. Examples include Amazon S3 and Google Cloud Storage.
- Block storage: Designed for high-performance databases and applications. Examples include AWS EBS and Azure Disk Storage.
- File storage: Used for file sharing and collaborative workspaces. Examples include Google Filestore and Azure Files.
Software
Cloud infrastructure uses various software to manage, automate, and optimize compute environments. Virtualization technologies like VMware, KVM, and Hyper-V are central to the efficient operation of cloud and infrastructure environments, allowing multiple operating systems to run on a single server. These tools are essential for enabling flexible, multi-tenant cloud-based infrastructure.
Cloud orchestration platforms such as Kubernetes and Terraform automate deployment and scaling processes. Meanwhile, cloud management interfaces like the AWS Management Console or Azure Portal allow administrators to monitor performance, enforce security, and optimize spending. Additionally, PaaS environments streamline the development of cloud-native applications, reinforcing the agility and scalability that define modern cloud infrastructure services.
What Are the Different Types of Cloud Infrastructure?
Different types of cloud infrastructure are SaaS, IaaS, PaaS, and FaaS. Each model represents different layers of abstraction within cloud infrastructure solutions, allowing businesses to select the approach that best suits their operational goals and technical capabilities. These models offer advantages like scalability, control, and development flexibility, forming the foundation for how cloud infrastructure management is implemented and optimized across industries.
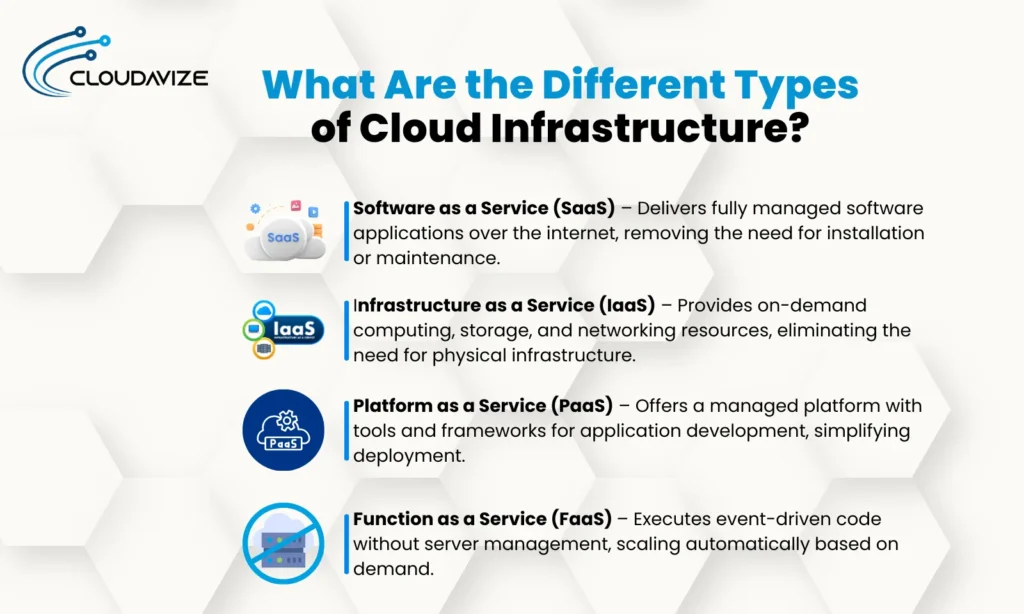
The 4 types of cloud infrastructure are discussed below.
SaaS (Software as a Service)
Accessing fully managed applications without handling infrastructure is what makes SaaS ideal for businesses seeking simplicity and speed. Delivered over the internet, Software as a Service allows organizations to use tools like Google Workspace, Salesforce, and Dropbox on a subscription basis. As a core component of cloud IT infrastructure, SaaS eliminates hardware dependencies and streamlines cloud infrastructure management for collaboration, CRM, and file storage.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
When businesses need complete control over computing resources without owning physical servers, IaaS provides the foundation. By leveraging virtualization, Infrastructure as a Service delivers scalable, on-demand access to core resources such as compute, storage, and networking. Leading platforms like AWS EC2 and Azure support cloud infrastructure as a service, giving teams flexibility, cost-efficiency, and robust disaster recovery in infrastructure as a service cloud computing environments.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
For developers focused on building applications without infrastructure concerns, PaaS offers a pre-configured environment that handles runtime, databases, and scaling. Tools like Google App Engine and Azure App Services reduce complexity, allowing faster deployment cycles. As part of modern cloud infrastructure services, Platform as a Service is essential for agile teams creating cloud-native apps within managed platforms.
FaaS (Function as a Service)
Running code in response to events, without managing servers, is the essence of FaaS, often called serverless computing. It enables granular scaling and cost-effective execution using services like AWS Lambda and Azure Functions. As an evolution of cloud infrastructure solutions, Function as a Service reduces operational overhead and aligns with microservices and event-driven architectures in dynamic business environments.
What Are the Architectures of Cloud Infrastructure?
The three architectures of cloud infrastructure are public, private, and hybrid cloud. Each cloud architecture offers distinctive advantages based on security, scalability, and flexibility needs. Before opting for a cloud architecture, businesses should consider various aspects like cost, control, regulatory requirements, and workload type.
Understanding the three types of cloud architectures enables organizations to optimize their cloud strategy for efficiency and performance.
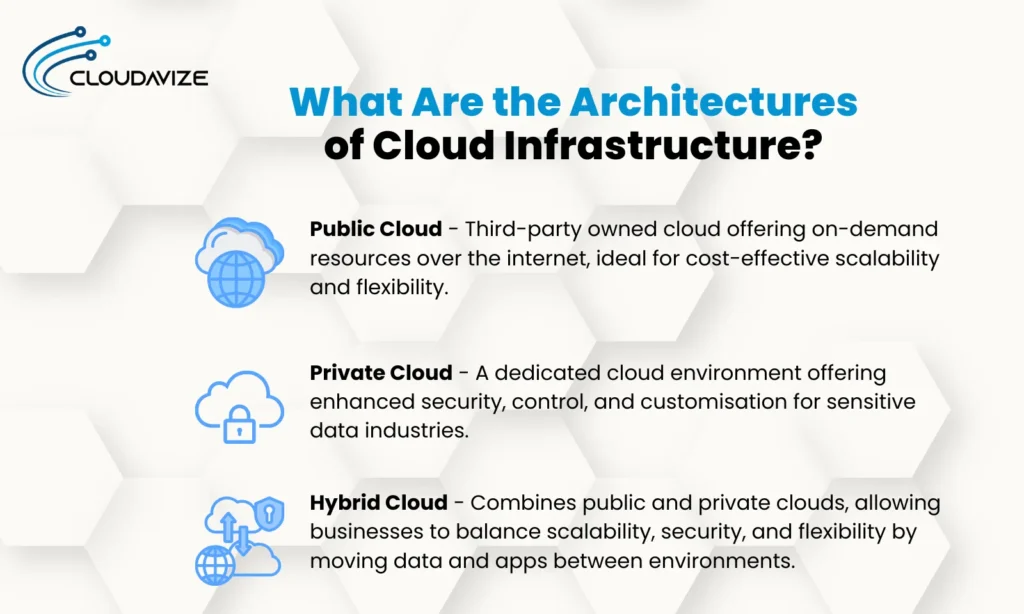
Public Cloud
Owned and managed by third-party providers, public cloud offers on-demand resources over the internet. Businesses can use services like storage, networking, and virtual machines without maintaining physical hardware. Because of its cost-effectiveness, this cloud infrastructure is ideal for startups and enterprises.
Leading providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud deliver high-performance cloud infrastructure as a service, supported by centralized cloud infrastructure management tools. This architecture is particularly well-suited for startups, e-commerce platforms, and enterprises running dynamic workloads that demand flexibility and global reach.
Private Cloud
A private cloud is a dedicated environment with exclusive access to computing resources, making it ideal for businesses that prioritize security, compliance, and custom configuration. It is often used by organizations in sectors like finance, healthcare, and government, where data sensitivity and regulatory standards are non-negotiable.
This model enhances control over cloud infrastructure management and allows for advanced customization of storage, computing, and access protocols. Although it involves higher upfront costs, private cloud remains a vital part of secure, high-performance cloud IT infrastructure, offering long-term value for enterprises that demand data sovereignty and strict governance.
Hybrid Cloud
Combining the benefits of both public and private models, hybrid cloud architecture supports seamless data and application movement across environments. It provides a unified approach to cloud infrastructure solutions, allowing businesses to store critical data privately while leveraging the scalability of public cloud for less sensitive workloads.
Hybrid models enable strategic cloud infrastructure management through integration and workload balancing across platforms. They support multi-cloud strategies, enhance flexibility, and help businesses optimize their infrastructure spend. This makes hybrid cloud an effective architecture for achieving both agility and compliance in cloud infrastructure as a service environments.
What’s the Difference Between Cloud Infrastructure and Cloud Computing?
Cloud infrastructure comprises the physical and virtual resources that power cloud environments, whereas cloud computing delivers software, platforms, and services over the internet, utilizing cloud infrastructure for hosting, processing, and data management.
Cloud infrastructure is the underlying framework that provides the necessary computing power, storage, and networking capabilities. In contrast, cloud computing is the operational layer that utilizes this infrastructure.
Cloud Infrastructure Vs. Cloud Computing
| Aspect | Cloud Infrastructure | Cloud Computing |
| Definition | The hardware and virtualized resources enabling cloud environments. | The services and applications running on the cloud infrastructure. |
| Focus | Provides computing power, storage, and networking capabilities. | Enables data processing, software execution, and automation. |
| Components | Servers, storage, networking, virtualization tools. | SaaS, PaaS, IaaS, databases, application frameworks. |
| Usage | Supports cloud computing operations. | Delivers scalable, on-demand computing services. |
| Management | Managed by cloud providers or IT teams for resource allocation. | Managed by users, developers, or businesses for running applications. |
| Examples | AWS EC2, Google Cloud Storage, Microsoft Azure VM. | Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Google Workspace, Salesforce, AWS Lambda. |
What Are the Benefits of Cloud Infrastructure?
The key benefits of cloud infrastructure include cost efficiency, scalability, high availability, security, and flexibility, making it an essential pillar of modern IT operations. Implementing cloud resources helps businesses minimize costs, improve reliability, and seamlessly scale operations while enhancing operational agility.
Cost Efficiency
Cloud infrastructure follows a pay-as-you-go model, which eliminates the need for expensive hardware investment, reducing operational costs. Businesses pay only for the resources they actively use, avoiding unnecessary expenses. This approach allows effective budget allocation, enabling the organization to reinvest the saved capital into innovation and business growth.
According to Zippia, 82% of SMBs lowered their IT costs after migrating to an IT infrastructure. For example, integrating Amazon OpenSearch Service helped Dream11, India’s largest fantasy sports platform, enhance performance while reducing infrastructure expenses.
Scalability
With cloud infrastructure, businesses can easily scale computing resources up or down based on real-time demand. This eliminates the need to overprovision hardware for peak usage periods. As cloud platforms allow automatic scaling, companies can use only the necessary resources to maintain optimal performance. Such elasticity helps e-commerce, media streaming, and financial services cruise easily during seasonal demand fluctuations.
Cloud infrastructure provides efficient and scalable resource management, allowing companies to adjust easily to sudden traffic spikes while optimizing costs. In 2020, Shopify scaled its operations and generated $5.1 billion in Black Friday sales without service interruptions.
High Availability and Redundancy
Cloud providers enhance high availability by distributing workloads across global data centers, reducing downtime and ensuring continuous service delivery. According to Patricia T. Endo et al., companies achieve high availability when annual downtime stays below 5.25 minutes. This level of reliability is essential for mission-critical applications like banking, healthcare, and SaaS platforms.
Leveraging distributed infrastructure further strengthens uptime and operational efficiency. For example, Siemens integrated AWS Lambda into its power plant operations, improving reliability, increasing critical alerts by 90%, and significantly reducing operational noise.
Security
Cloud infrastructure providers implement robust security measures, such as encryption, firewalls, identity access management (IAM), and multi-factor authentication (MFA), to safeguard sensitive data from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber threats. For example, using MFA on accounts protects them 99 out of 100 times from being hacked. Additionally, cloud providers help maintain compliance with industry-specific regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2, avoiding legal actions while ensuring data protection.
Cloud security also delivers tangible benefits, with McAfee’s Cloud Adoption and Risk Report revealing that 52% of companies experienced better security in the cloud. For example, Coca-Cola enhanced its security infrastructure by partnering with IBM Cloud, leveraging IoT integration and real-time analytics to strengthen vending operations while ensuring data integrity.
Disaster Recovery and Backup
Automated disaster recovery in the cloud means that if your hardware fails, you are hit by a cyber attack, or you accidentally delete something, your data can be recovered quickly. With cloud infrastructure providing centralized backup and recovery, the risk of catastrophic data loss is minimized.
According to FEMA, 43% of SMBs that experience a disaster never reopen, and 29% of those that open fail within 2 years. Unlike traditional backup systems, you do not need to intervene manually, which reduces downtime and business disruption. These solutions offer geo redundancy, which stores your backup data in multiple locations so you do not risk losing everything even after a disaster.
Automatic Updates and Maintenance
Cloud providers handle software updates, security patches, and performance tuning for you, eliminating manual IT work. This ensures that businesses always operate on the latest technology without worrying about system vulnerabilities. Automatic updates proactively fix potential exploits before they become threats, significantly reducing the risk of cyberattacks. For example, Microsoft’s Azure Update Management auto-deploys patches to Windows systems, so security fixes and performance improvements are applied seamlessly with minimal IT effort.
Beyond security, automatic updates also include performance optimizations and bug fixes, ensuring systems remain stable and efficient without requiring user intervention. Cloud providers update their platforms and services continuously, fixing bugs and applying security improvements without disrupting your business.
Global Reach
Cloud infrastructure allows you to serve customers globally with data centers in multiple regions. This global reach means your applications and services are highly available and have low latency, no matter where your customers are.
For example, Amazon Web Services (AWS) has 36 regions with 114 Availability Zones, so you can deploy closer to your customers, reduce latency, and increase reliability. Similarly, Microsoft Azure has over 60+ regions and 300+ data centers, making it one of the biggest cloud networks for global expansion. With this much coverage, you can go global without having to invest in physical IT infrastructure across multiple countries.
Flexibility
Cloud infrastructure offers unmatched flexibility, allowing businesses to customize resources to their needs. Either for AI workloads or basic cloud storage, cloud platforms provide scalable solutions that can be deployed in the shortest duration. This agility allows companies to innovate and roll out new services fast, without months of procurement cycles. For example, Sunrise Communications AG collaborated with Red Hat to build a hybrid cloud-ready platform, reducing time-to-market by 75%.
Cloud computing allows businesses to access computing resources quickly, improving agility and operational efficiency. Spotify migrated 1,200 services to Google Cloud, ensuring seamless streaming for over 271 million users. This highlights the power of flexibility and scalability in driving business success.
What Are the Challenges of Cloud Infrastructure?
The challenges of cloud infrastructure include security risks, downtime, vendor lock-in, and cost management issues. While cloud services offer scalability and efficiency, it is essential to address these hurdles to ensure secure, reliable, and cost-effective operations.
Below are the 4 critical challenges of cloud infrastructure that must be addressed to maximize benefits while minimizing risks.
- Security and Privacy
Storing sensitive data on third–party cloud servers poses the risk of data breaches, unauthorized access, and privacy violations. Even though cloud providers offer security measures like firewalls, encryption, and security protocols, the responsibility of data and applications over the cloud still falls on organizations, raising accountability issues. Also, the necessity of adhering to industry regulation like GDPR and HIPAA adds an extra layer of complexity to cloud security.
Solutions include implementing end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication (MFA), strict access controls, and regular security audits to safeguard data. Adopting Zero Trust architecture also helps minimize security vulnerabilities.
- Downtime and Service Interruptions
Despite the promise of high availability, cloud providers cannot eliminate unexpected outages that arise from network failures, cyberattacks, or technical issues. These operational issues lead to significant financial losses, productivity setbacks, and disrupted customer experiences for businesses. The reliance of cloud services on internet connectivity further amplifies the risk of accessibility issues.
To mitigate downtime and service interruptions, businesses should deploy multi-region cloud architectures, automated failover mechanisms, and backup solutions. They should conduct regular disaster recovery testing to ensure business continuity after a disruption.
- Vendor Lock-In
Many cloud infrastructure service providers use proprietary technologies and unique configurations that make it challenging for businesses to switch to a different provider. The difficulty of data migration, along with the high cost, technical complexity, and potential downtime, forces businesses to stick with a single provider, even though their service and products are inferior.
To break the shackles of customer or proprietary lock-in, businesses should adopt a multi-cloud or hybrid cloud approach that helps disperse workloads across multiple providers and reduce reliance on a single vendor. Using open-source tools and containerization technologies like Kubernetes improves portability across cloud environments.
- Cost Management
Because cloud services operate on a pay-as-you-go model, lack of proper monitoring and optimization risks the probability of unexpected cost spikes. Expenses can escalate rapidly when resources remain idle and resources are underutilized. This makes budgeting difficult. Without proper cost control, organizations are compelled to overspend on cloud resources, leading to budget restraints for other core operations.
One way to ensure proper cost management is to track expenses using cloud cost management tools like AWS Cost Explorer, Azure Cost Management, and Google Cloud Billing. Implementing auto-scaling, resource tagging, and budget alerts helps optimize cloud spending, while conducting regular cost audits and rightsizing resources prevent unnecessary expenses.
What Tools are used for Managing Cloud Infrastructure?
Tools used for managing cloud infrastructure are essential cloud management platforms, automation tools, monitoring tools, and cost management tools. These specialized tools help deploy, monitor, and optimize resources efficiently, enabling businesses to automate provisioning, track performance, and ensure security across cloud environments.
Below are key categories of tools used for cloud infrastructure management
- Cloud Management Platforms
- AWS Management Console – Web-based interface for managing AWS resources, monitoring, and configuration.
- Microsoft Azure Portal – Unified web platform for deploying, managing, and monitoring Azure services.
- Google Cloud Console – Web interface for managing Google Cloud resources, performance, and configurations.
- Configuration Management and Automation Tools
- Ansible – Agentless automation for configuration management and deployment.
- Puppet – Automates system configuration and application deployment.
- Chef – Manages and automates cloud infrastructure as code.
- Terraform – Open-source tool for infrastructure automation and provisioning.
- Monitoring and Logging Tools
- Prometheus – Open-source monitoring for cloud infrastructure.
- Grafana – Visualization tool for monitoring data.
- AWS CloudWatch – Monitors AWS resources and applications.
- Datadog – Cloud monitoring and security platform.
- Security and Compliance Tools
- HashiCorp Vault – Secrets management and encryption.
- AWS IAM (Identity & Access Management) – Manages access to AWS resources.
- AccuKnox – Kubernetes security and cloud workload protection.
- Cost Management and Optimization Tools
- AWS Cost Explorer – Analyzes AWS spending and usage trends.
- Google Cloud Cost Management – Tracks and manages GCP costs.
- CloudHealth by VMware – Provides multi-cloud cost optimization.
Why Choose Cloudavize for Your Cloud Infrastructure Needs?
Reliable cloud infrastructure is essential for businesses to achieve scalability, security, and cost efficiency while minimizing the complexities of on-premises IT management. A well-optimized cloud environment enhances performance, flexibility, and resilience, enabling companies to adapt quickly to changing demands and drive innovation.Navigating the complexities of cloud deployment and management requires the right expertise. This is where Cloudavize provides value by offering tailored cloud solutions that ensure seamless integration, robust security, and operational efficiency. With expertise in public, private, and hybrid cloud environments, Cloudavize helps businesses unlock the full potential of the cloud while keeping infrastructure secure, scalable, and cost-effective.



